Class 06 Project Tracing the path
Instructions :
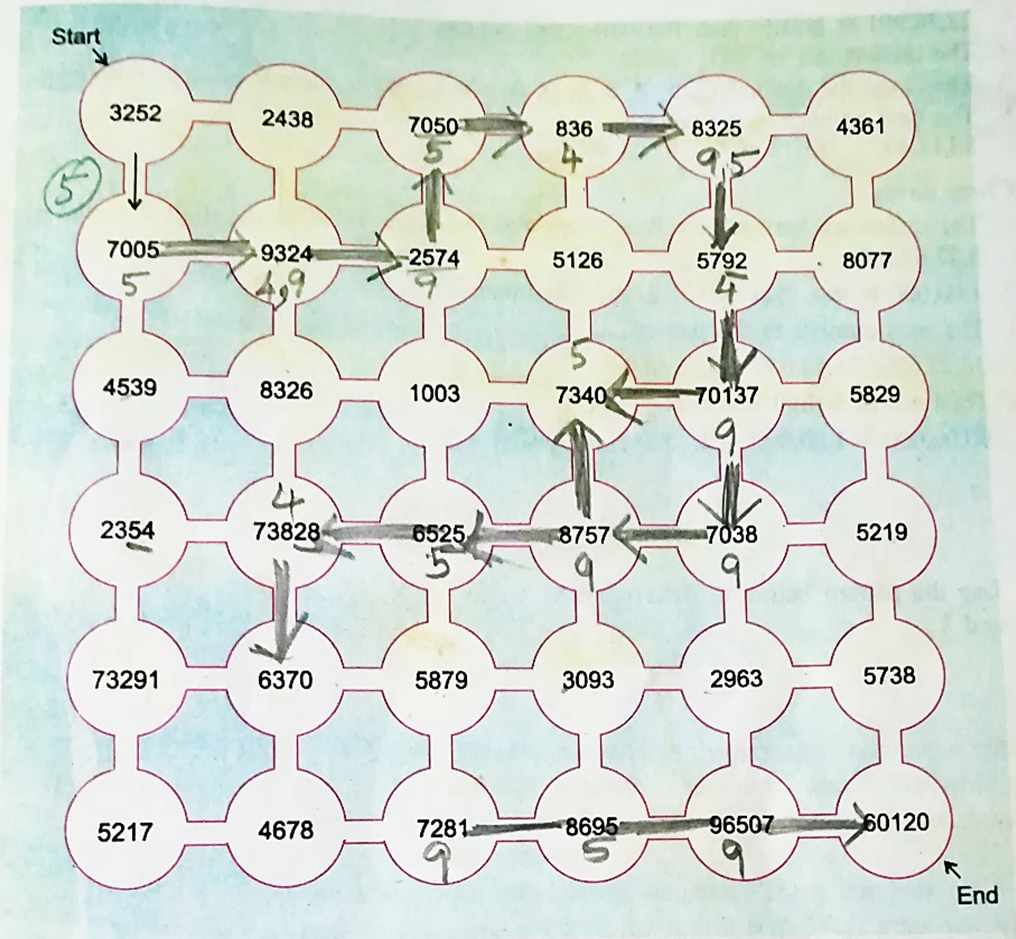
You have to find a path from starting point to the end point, always moving to a circle which is divisible by any one number 4, 5 or 9.
Procedure:
Starting number is 3252.
From 3252, you can move either to 7005 or 2438. But, 2438 is not divisible by any of the numbers 4, 5 or 9.
However, 7005 is divisible by 5, so, we move to 7005.
2. From 7005 the two options are 9324 and 4539. But, 9324 is divisible, by both 4 and 9 and 4539 is not divisible by any one of the numbers 4, 5 and 9. so we move to 9324.
3. Go on to reach the end point.
4. Do you find more than one path?
PROJECT 2 – TRACING THE PATH -Solution
Procedure: 3252 is divisible by 4.
1. 7005 is divisible by 5.
2. 9324 is divisible, by both 4 and 9
3. 9324 is divisible by 4 & 9.
4. 2574 is divisible by 9.
5. 7050 is divisible by 5.
6. 836 is divisible by 4.
7. 8325 is divisible by 9 & 5.
8. 5792 is divisible by 4.
9. 70137 is divisible by 9.
10. 7340 is divisible by 5.
11. 7038 is divisible by 9.
12. 8757 is divisible by 9.
13. 8525 is divisible by 5.
14. 73828 is divisible by 4.
15. 6370 is divisible by 5
16. 4670 is divisible by 5.
17. 7281 is divisible by 9.
18. 8695 is divisible by 5.
19. 96507 is divisible by 9
20. 60120 is divisible by 5 &9.
reach the end point
Do you find more than one path? Yes.