ACTIVITY – BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEAS
Objective:
On the line segment of length 5 cm on a paper:
(a) to make a perpendicular line from a point on the given time by paper folding,
(b) to make a perpendicular line to the given line from a point outside the line by paper folding.
(c) To make two intersecting lines by paper folding
(d) to make two parallel lines by paper folding.
Materials Required:
Tracing papers, colour pencils, geometry box, etc.
(a) to make a perpendicular line from a point on the given time by paper folding,
On a tracing paper, draw a line segment AB = 5 cm. Mark a point P on AB
2. Fold the tracing paper at P such that PB falls along PA.
3. Unfold the tracing paper and draw a line XY along the crease, which passes through P. ∟APX = 90°
(b) to make a perpendicular line to the given line from a point outside the line by paper folding.
4. On a tracing paper, draw a line segment AB = 5 cm.
Mark a point O above or below the line segment AB.
5.Fold the tracing paper such that the folding line passes through O and the two parts of AB coincide.
6.Unfold the tracing paper and draw a line along the crease, which passes through O. ∟OPA = 90°
(c) To make two intersecting lines by paper folding
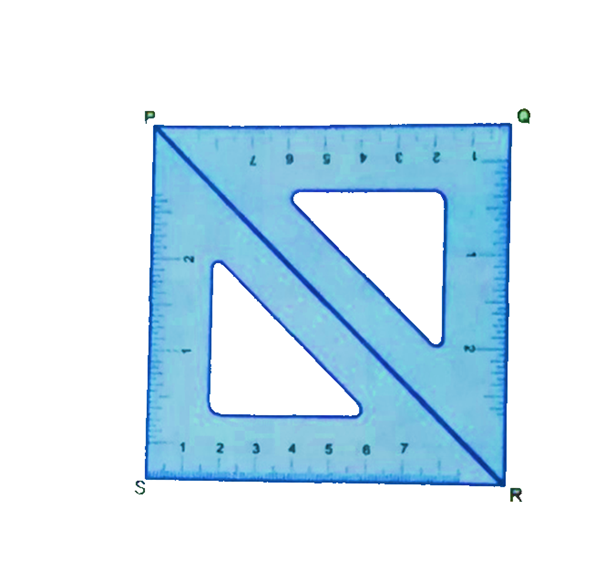
7. Take a sheet of tracing paper PQRS of dimensions 15 cm x 15 cm. In the middle of it draw a line segment AB = 5 cm.
8. Fold the tracing paper, such that SR and RQ coincide.
9. Unfold the tracing paper and draw a line along the crease.
10. Fold the tracing paper such that RS and SP coincide.
11. Unfold the tracing paper and draw a line along the crease.
(d) To make two parallel lines by paper folding.
12. Take a sheet of tracing paper PQRS. On it draw a line segment AB = 5 cm.
13. Fold the tracing paper such that the folding line falls along AB.
14. Again fold the tracing paper such that AB (first folding line)falls along PQ
15. Unfold the tracing paper and draw lines along the creases.
Observations:
On measuring ∠APX, in figure 3, we find that it measures 90 °. Hence, XY is a line perpendicular to AB and passing through P.
2. On measuring ∠OPA, in figure 6, we find that it measures 90 °. Hence, OP is a line perpendicular to AB and passing through O.
3. In figure 11, lines PR and SQ intersect at O. Also, the point of intersection of AB and PR is L and the point of intersection of AB and SQ is M.
4. In figure 15, if we extend each of the lines XY, AB and LM, no two lines intersect. It means XY, AB and LM are parallel lines.