9 Algebraic Expressions And Identities
9.1 What Are Expressions
9.2 Terms Factors And Coefficients
9.3 Monomials Binomials And Polynomials
9.4 Like And Unlike Terms
9.5 Addition And Subtraction Of Algebraic Expressions
9.6 Multiplication Of Algebraic Expressions
9.7 Multiplying A Monomial Monomial
9.7.1 Multiplying Two Monomials
9.7.2 Multiplying Three Or More Monomials
9.8 Multiplying A Monomial By A Polynomial
9.8.1 Multiplying Monomial By A Binomial
9.8.2 Multiplying Monomial By A Trinomial
9.9 Multiplying A Polynomial By A Polynomial
9.9.1 Multiplying A Binomial By Binomial
9.9.2 Multiplying Binomial By Trinomial
9.10 What Is An Identity
9.11 Standard Identities
9.12 Applying Identities10 Visualising Solid Shapes
Example 1: Add: 7xy + 5yz – 3zx, 4yz + 9zx – 4y , –3xz + 5x – 2xy.
Solution:7xy + 5yz –3zx + 4yz + 9zx – 4y + –2xy – 3zx + 5x =
5xy + 9yz +3zx + 5x – 4yExample 2: Subtract 5x2 – 4y2 + 6y – 3 from 7x2 – 4xy + 8y2 + 5x – 3y. Solution:
7x2 – 4xy + 8y2 + 5x – 3y
5x2 – 4y2 + 6y – 31. Identify he terms, their coefficients for each of the following expressions.
(i) 5xyz2 – 3zy
(ii) 1 + x + x2
(iii) 4x2y2 – 4x2y2z2 + z2
(iv) 3 – pq + qr – rp
(v) x/2 + y/2 − xy
(vi) 0.3a – 0.6ab + 0.5b
2. Classify the following polynomials as monomials, binomials, trinomials. Which polynomials do not fit in any of these three categories?
x + y, 1000, x + x2 + x3 + x4, 7 + y + 5x, 2y – 3y2, 2y – 3y2 + 4y3, 5x – 4y + 3xy, 4z – 15z2, ab + bc + cd + da, pqr, p2q + pq2, 2p + 2q
3. Add the following.
(i) ab – bc, bc – ca, ca – ab
(ii) a – b + ab, b – c + bc, c – a + ac
(iii) 2p2q2 – 3pq + 4, 5 + 7pq – 3p2q2
(iv) l2 + m2, m2 + n2, n2 + l2, 2lm + 2mn + 2nl
4. (a) Subtract 4a – 7ab + 3b + 12 from 12a – 9ab + 5b – 3
(b) Subtract 3xy + 5yz – 7zx from 5xy – 2yz – 2zx + 10xyz
(c) Subtract 4p2q – 3pq + 5pq2 – 8p + 7q – 10 from 18 – 3p – 11q + 5pq – pq2 + 5p2q
Example 3: Complete the table for area of a rectangle with given length and breadth.
Solution:
length breadth area
3x 5y 3x × 5y = 15xy
9y 4y2..............
4ab 5bc ..............
2l2m 3lm2..............
Example 4: Find the volume of each rectangular box with given length, breadth and height.
length breadth height
(i) 2ax 3by 5cz
(ii) m2n n2p p2m
(iii) 2q 4q2 8q3
Solution: Volume = length × breadth × height
Hence, for (i) volume = (2ax) × (3by) × (5cz) = 2 × 3 × 5 × (ax) × (by) × (cz) = 30abcxyz
for (ii) volume = m2n × n2p × p2m = (m2 × m) × (n × n2) × (p × p2) = m3n3p3
for (iii) volume = 2q × 4q2 × 8q3 = 2 × 4 × 8 × q × q2 × q3 = 64q6
EXERCISE 9.2
1. Find the product of the following pairs of monomials.
(i) 4, 7p
(ii) – 4p, 7p
(iii) – 4p, 7pq
(iv) 4p3, – 3p
(v) 4p, 0
2. Find the areas of rectangles with the following pairs of monomials as their lengths and breadths respectively.
(p, q); (10m, 5n); (20x2, 5y2); (4x, 3x2); (3mn, 4np)
3. Complete the table of products.
First monomial → Second monomial ↓
4. Obtain the volume of rectangular boxes with the following length, breadth and height respectively.
(i) 5a, 3a2, 7a4
(ii) 2p, 4q, 8r
(iii) xy, 2x2y, 2xy2
(iv) a, 2b, 3c
5. Obtain the product of
(i) xy, yz, zx
(ii) a, – a2, a3
(iii) 2, 4y, 8y2, 16y3
(iv) a, 2b, 3c, 6abcFind the product:
(4p2 + 5p + 7) × 3p(i) x (x – 3) + 2 = x2 – 3x + 2
For x = 1, x2 – 3x + 2 = (1)2 – 3 (1) + 2
= 1 – 3 + 2 = 3 – 3 = 0
(ii) 3y (2y – 7) – 3 (y – 4) – 63 = 6y2 – 21y – 3y + 12 – 63
= 6y2 – 24y – 51
For y = –2, 6y2 – 24y – 51 = 6 (–2)2 – 24(–2) – 51
= 6 × 4 + 24 × 2 – 51
= 24 + 48 – 51 = 72 – 51 = 21
Example 6: Add
(i) 5m (3 – m) and 6m2 – 13m
(ii) 4y (3y2 + 5y – 7) and 2 (y3 – 4y2 + 5)
Solution:
(i) First expression = 5m (3 – m) = (5m × 3) – (5m × m) = 15m – 5m2
Now adding the second expression to it,15m – 5m2 + 6m2 – 13m = m2 + 2m
(ii) The first expression
= 4y (3y2 + 5y – 7) = (4y × 3y2) + (4y × 5y) + (4y × (–7))
= 12y3 + 20y2 – 28y
The second expression = 2 (y3 – 4y2 + 5) = 2y3 + 2 × (– 4y2) + 2 × 5 =2y3 – 8y2 + 10
Adding the two expressions,
12y3 + 20y2 – 28y + 2y3 – 8y2 + 10 =14y3 + 12y2 – 28y + 10
Example 7: Subtract 3pq (p – q) from 2pq (p + q).
Solution: We have 3pq (p – q) = 3p2q – 3pq2 and
2pq (p + q) = 2p2q + 2pq2
Subtracting,
2p2q + 2pq2
3p2q – 3pq2
– +
– p2q + 5pq2EXERCISE 9.3
1. Carry out the multiplication of the expressions in each of the following pairs.
(i) 4p, q + r
(ii) ab, a – b
(iii) a + b, 7a2b2
(iv) a2 – 9, 4a
(v) pq + qr + rp, 0
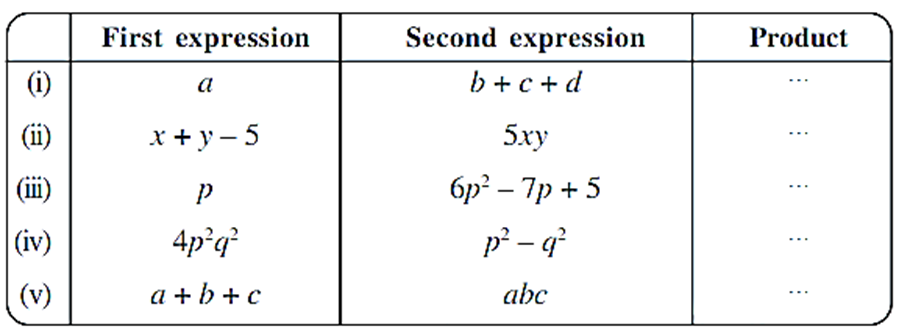
2. Complete the table.
First expression Second expression Product
(i) a b + c + d. . .
(ii) x + y – 5 5xy . . .
(iii) p 6p2 – 7p + 5 . . .
(iv) 4p2q2 p2 – q2 . . .
(v) a + b + c abc . . .
(c) Subtract: 3l (l – 4 m + 5 n) from 4l ( 10 n – 3 m + 2 l )
(d) Subtract: 3a (a + b + c ) – 2 b (a – b + c) from 4c ( – a + b + c )Solution:
(i) (x – 4) × (2x + 3) = x × (2x + 3) – 4 × (2x + 3)
= (x × 2x) + (x × 3) – (4 × 2x) – (4 × 3)
= 2x2 + 3x – 8x – 12
= 2x2 – 5x – 12
(ii) (x – y) × (3x + 5y) = x × (3x + 5y) – y × (3x + 5y)
= (x × 3x) + (x × 5y) – (y × 3x) – ( y × 5y)
= 3x2 + 5xy – 3yx – 5y2 = 3x2 + 2xy – 5y2
Example 9: Multiply
(i) (a + 7) and (b – 5) (ii) (a2 + 2b2) and (5a – 3b)
Solution:
(i) (a + 7) × (b – 5) = a × (b – 5) + 7 × (b – 5)
= ab – 5a + 7b – 35
(ii) (a2 + 2b2) × (5a – 3b) = a2 (5a – 3b) + 2b2 × (5a – 3b)
= 5a3 – 3a2b + 10ab2 – 6b3Solution: (a + b) (2a – 3b + c)
= a (2a – 3b + c) + b (2a – 3b + c)
= 2a2 – 3ab + ac + 2ab – 3b2 + bc
= 2a2 – ab – 3b2 + bc + ac (Note, –3ab and 2ab are like terms)
and (2a – 3b) c = 2ac – 3bc
Therefore,
(a + b) (2a – 3b + c) – (2a – 3b) c
= 2a2 – ab – 3b2 + bc + ac – (2ac – 3bc)
= 2a2 – ab – 3b2 + bc + ac – 2ac + 3bc
= 2a2 – ab – 3b2 + (bc + 3bc) + (ac – 2ac)
= 2a2 – 3b2 – ab + 4bc – acEXERCISE 9.4
1. Multiply the binomials. (i) (2x + 5) and (4x – 3)
(ii) (y – 8) and (3y – 4)
(iii) (2.5l – 0.5m) and (2.5l + 0.5m)
(iv) (a + 3b) and (x + 5)
(v) (2pq + 3q2) and (3pq – 2q2)
(vi)
2. Find the product.
(i) (5 – 2x) (3 + x)
(ii) (x + 7y) (7x – y)
(iii) (a2 + b) (a + b2)
(iv) (p2 – q2) (2p + q)
3. Simplify.(i) (x2 – 5) (x + 5) + 25
(ii) (a2 + 5) (b3 + 3) + 5
(iii) (t + s2) (t2 – s)
(iv) (a + b) (c – d) + (a – b) (c + d) + 2 (ac + bd)
(v) (x + y)(2x + y) + (x + 2y)(x – y)
(vi) (x + y)(x2 – xy + y2)
(vii) (1.5x – 4y)(1.5x + 4y + 3) – 4.5x + 12y
(viii) (a + b + c)(a + b – c)(i) (2x + 3y)2 = (2x)2 + 2(2x) (3y) + (3y)2[Using the Identity (I)]
= 4x2 + 12xy + 9y2
(2x + 3y)2 = (2x + 3y) (2x + 3y)
= (2x) (2x) + (2x) (3y) + (3y) (2x) + (3y) (3y)
= 4x2 + 6xy + 6 yx + 9y2(as xy = yx)
= 4x2 + 12xy + 9y2= 1002 + 2 × 100 × 3 + 32(Using Identity I)
= 10000 + 600 + 9 = 10609
Example 12: Using Identity (II),
find (i) (4p – 3q)2(ii) (4.9)2
Solution:
(i) (4p – 3q)2 =(4p)2 – 2 (4p) (3q) + (3q)2[Using the Identity (II)]
= 16p2 – 24pq + 9q2
(ii) (4.9)2 =(5.0 – 0.1)2 = (5.0)2 – 2 (5.0) (0.1) + (0.1)2
= 25.00 – 1.00 + 0.01 = 24.01
Example 13: Using Identity (III), find
(ii) 9832 – 172 = (983 + 17) (983 – 17)
[Here a = 983, b =17, a2 – b2 = (a + b) (a – b)] Therefore, 9832 – 172 = 1000 × 966 = 966000
(iii) 194 × 206 = (200 – 6) × (200 + 6) = 2002 – 62
= 40000 – 36 = 39964
Example 14: Use the Identity (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab to find the following:
(i) 501 × 502 (ii) 95 × 103
Solution:
(i) 501 × 502 = (500 + 1) × (500 + 2)
= 5002 + (1 + 2) × 500 + 1 × 2
= 250000 + 1500 + 2 = 251502
(ii) 95 × 103 = (100 – 5) × (100 + 3)
= 1002 + (–5 + 3) × 100 + (–5) × 3
= 10000 – 200 – 15 = 9785
EXERCISE 9.5
1. Use a suitable identity to get each of the following products.
(i) (x + 3) (x + 3)
(ii) (2y + 5) (2y + 5)
(iii) (2a – 7) (2a – 7)
(iv) (3a – 1/2) (3a – 1/2)
(v) (1.1m – 0.4) (1.1m + 0.4)
(vi) (a2 + b2) (– a2 + b2)
(vii) (6x – 7) (6x + 7)
(viii) (– a + c) (– a + c)
(ix)
2. Use the identity (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab to find the following products. (i) (x + 3) (x + 7)
(ii) (4x + 5) (4x + 1)
(iii) (4x – 5) (4x – 1)
(iv) (4x + 5) (4x – 1)
(v) (2x + 5y) (2x + 3y)
(vi) (2a2 + 9) (2a2 + 5)
(vii) (xyz – 4) (xyz – 2)
3. Find the following squares by using the identities.
(i) (b – 7)2
(ii) (xy + 3z)2
(iii) (6x2 – 5y)2
(vi)
(v) (0.4p – 0.5q)2
(vi) (2xy + 5y)2
4. Simplify.
(i) (a2 – b2)2
(ii) (2x + 5)2 – (2x – 5)2
(iii) (7m – 8n)2 + (7m + 8n)2
(iv) (4m + 5n)2 + (5m + 4n)2
(v) (2.5p – 1.5q)2 – (1.5p – 2.5q)2
(vi) (ab + bc)2 – 2ab2c
(vii) (m2 – n2m)2 + 2m3n2
5. Show that.
(i) (3x + 7)2 – 84x = (3x – 7)2
(ii) (9p – 5q)2 + 180pq = (9p + 5q)2
(iii) +
(iv) (4pq + 3q)2 – (4pq – 3q)2 = 48pq2
(v) (a – b) (a + b) + (b – c) (b + c) + (c – a) (c + a) = 0
6. Using identities, evaluate.
(i) 712
(ii) 992
(iii) 1022
(iv) 9982
(v) 5.22
(vi) 297 × 303
(vii) 78 × 82
(viii) 8.92
(ix) 10.5 × 9.5
7. Using a2 – b2 = (a + b) (a – b), find
(i) 512 – 492
(ii) (1.02)2 – (0.98)2
(iii) 1532 – 1472
(iv) 12.12 – 7.92
8. Using (x + a) (x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab,
find (i) 103 × 104
(ii) 5.1 × 5.2
(iii) 103 × 98
(iv) 9.7 × 9.8






No comments:
Post a Comment